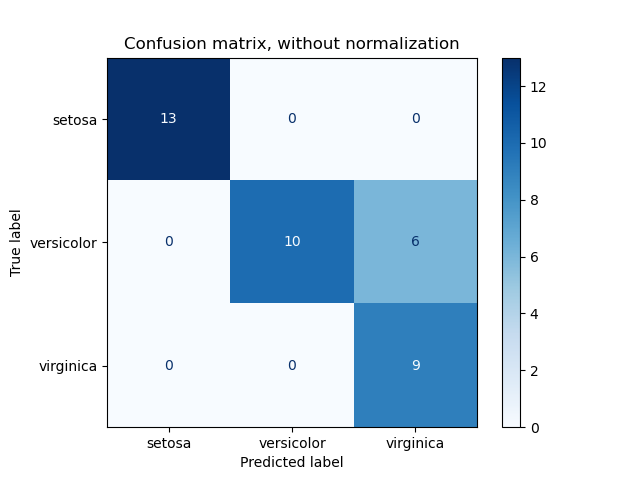
In machine learning, it is common for classifiers to make incorrect predictions. These incorrect predictions can be referred to as false prediction labels. Identifying false prediction labels is important because it can affect the accuracy of the classifier model by having control over the data.
Fortunately, there are ways to easily find these false prediction labels in a classifier machine learning model. But one way is to use the code I have provided in my project. The way I used it, involves creating a data frame of the true labels and the data set counters. Then, predict the model on test data and define the prediction labels. Finally, print the true label column with their counters and the predicted labels. By doing so, you can compare the true labels with the predicted labels and identify any discrepancies, which will help you determine the false prediction labels in the classifier machine learning model.
Find my code attached herewith, which can be incorporated into your model post-training for optimal results:
#Get the number of test data (Based on your test size)
num = 100
#Predict the model on test data and let it define the labels
pred_labels = model.predict(X_test)
#Create a data frame of test's true labels and the predicted lavbels
testdf=pd.DataFrame(X_test)
predictdf=pd.DataFrame(pred_labels)
#Just print the true label column with counters from your data set
print(testdf["Label"])
#See the predicted labels to compare
print(f"pred_probs for first {num} examples in format expected by cleanlab:")
print(pred_labels[:num])
Furthermore, this code enables you to export and preserve both the test data labels and predicted labels in a .csv file to easily compare them:
#In the code above make data frames from the true labels of testing data and the predicted labels.
#Now we can merge and save them in a single .csv file
check=[dftest,predict]
checklist = pd.concat(check,ignore_index=True)
checklist.to_csv("Checklist_of_false.csv")